The ABC’s of microSD and SD Cards
It used to be so simple. Just select a Class 10 card and you were good to go. Then came UHS speed classes, Video Speed Classes, and Application Performance Classes! There are so many symbols on a microSD card today, it looks like alphabet soup.
microSD and SD cards are two of the most popular storage form factors, due to their ease of integration, small size, low power consumption and performance. We will attempt to break down the different symbols and designations, to help you determine what type of card is the best for your application.
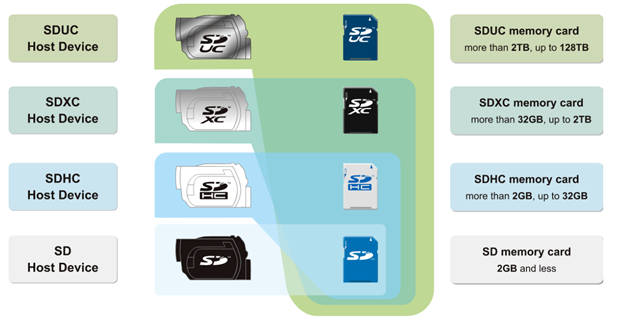
The first designation is based on the capacity of the card and compatibility with hosts:
Source: https://www.sdcard.org/
An SD Host device can only accept SD memory cards, which are 2GB or lower capacity. However, higher level host devices are backward compatible – for example, SDXC hosts can accept SD, SDHC and SDXC memory cards. This applies to both full size SD and microSD cards.
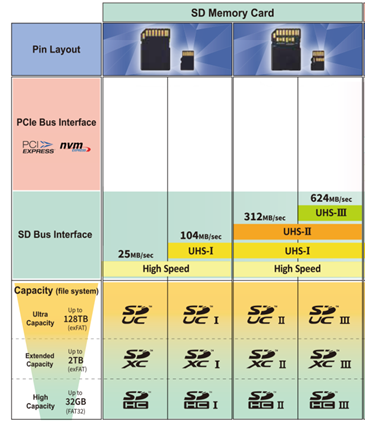
The next designation is bus interface speed. SD and microSD cards in 2GB and lower capacity points do not have designated speed classes, this begins at 4GB for SDHC.
Source: https://www.sdcard.org/
Cards that do not support UHS (Ultra High Speed) bus speed will just have the SDHC, SDXC or SDUC logo. UHS enabled cards will have a I, II or III, depending on the supported bus speed of 104, 312 or 624 MB/s, respectively. UHS-I and non-UHS cards will have standard 8 (microSD) or 9 contacts (SD), whereas UHS II and III cards have a second row of contacts to enable this high-speed functionality.
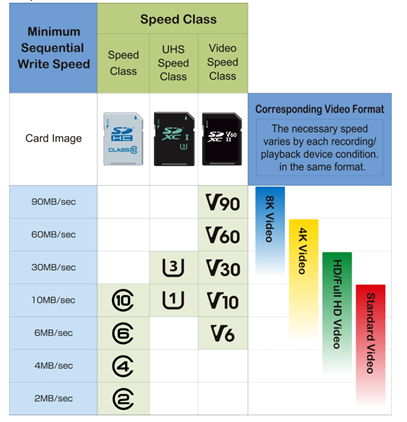
The next designation is speed class. There are three types of speed class – Speed Class, UHS Speed Class and Video Speed Class – which are indicated by symbols denoting the minimum sequential write speed. Depending on the type of data being written, especially high definition video, a higher performance card may be necessary to ensure continuous recording.
Source: https://www.sdcard.org/
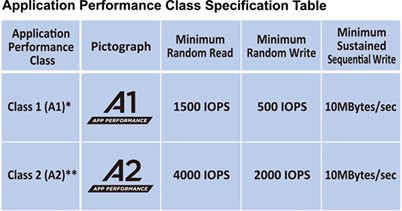
Further to these speed classes, which are mainly about sustained data rates for continuous video recording, there is Application Performance Class, which adds minimum random IOPS ratings (Inputs/Outputs Per Second) to a minimum sequential write speed. Application Speed Class is aimed at expansion storage for mobile devices, for holding, loading and running mobile apps, where both sequential and random performance is important.
Source: https://www.sdcard.org/
So, how do you determine what type of card you need? Answer a few simple questions:
- What does my host support? (SD, SDHC, SDXC or SDUC?)
- What capacity do I need?
- What bus interface speed does my host support?
- What type of data and data rate will I be writing to the card? i.e. 4K or 8K video, or small log file updates, etc.
- What sequential performance level (in MB/s) do I need?
- Do I need mainly sequential performance or is random IOPS also important?
Delkin recognizes that every application is unique. Let us help you identify the best SD or microSD solution for your specific application.
ORDER DELKIN INDUSTRIAL FLASH STORAGE TODAY through our distribution partner Newark.
For Europe Contact Our Partner Farnell
 Login
Login Register
Register